I. Brief (Geoinformatics | Geomatics | Remote Sensing Satellite | GIS)
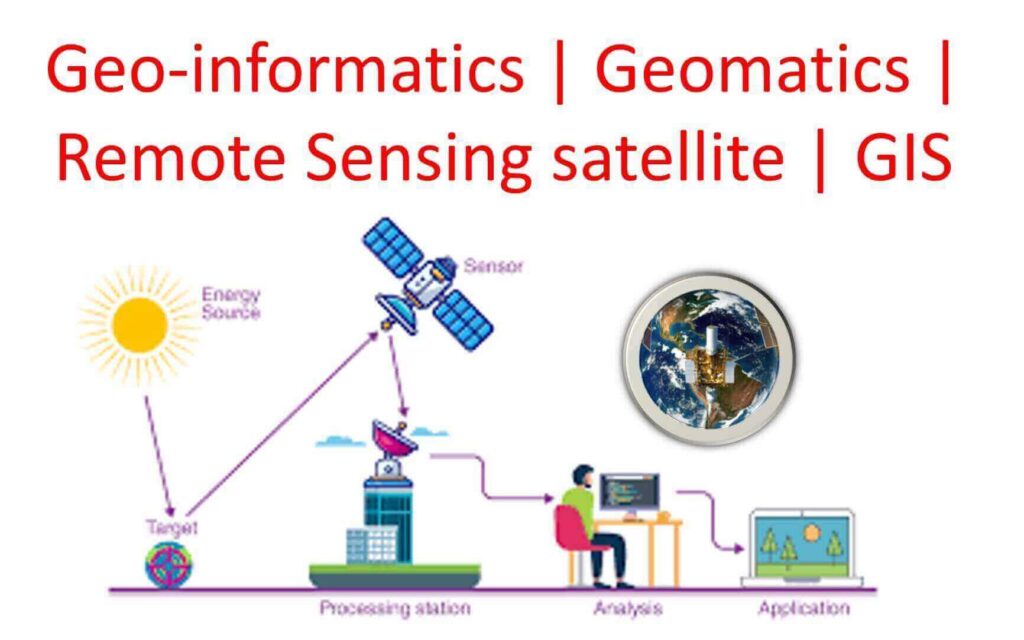
A. Introduction to Geoinformatics
Geoinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that combines geospatial technology, computer science, and data analysis to study and understand the Earth’s physical and social systems. It is a powerful tool that enables us to map, analyze, and visualize spatial data to derive insights and make informed decisions.
B. Purpose and Significance of the Essay
The purpose of this essay is to provide an overview of Geoinformatics, its history, applications in various industries, and the methods and tools used in the field. The essay aims to highlight the importance and impact of Geoinformatics in today’s society.
II. Body Paragraphs
A. Definition and History of Geoinformatics
Key Concepts and Terminologies
Geoinformatics encompasses a wide range of concepts and terminologies, including spatial data, geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing (RS), global positioning systems (GPS), and data analytics. Spatial data refers to any data that has a geographic component, such as location, elevation, and distance. GIS is a software tool that enables the storage, analysis, and visualization of spatial data. RS involves the use of sensors to capture data from a distance, such as from satellites or aircraft. GPS is a network of satellites that provides precise location data. Data analytics involves the use of statistical and computational methods to extract insights from large volumes of data.
Historical Development of the Field
Geoinformatics has its roots in cartography, surveying, and geography. The development of computer technology and GIS software in the 1960s and 1970s enabled the analysis of large volumes of spatial data. In the 1980s and 1990s, the use of RS and GPS expanded the scope of Geoinformatics. Today, Geoinformatics is a rapidly evolving field that is at the forefront of technological innovation.
B. Applications of Geoinformatics in Various Industries
Agriculture and Natural Resource Management
Geoinformatics is widely used in agriculture to optimize crop yield, reduce environmental impact, and improve food security. It is also used in natural resource management to monitor land use, track changes in forest cover, and manage water resources.
Urban Planning and Development
Geoinformatics plays a crucial role in urban planning and development by providing insights into land use, transportation, and infrastructure. It is used to analyze patterns and trends, identify optimal locations for infrastructure, and plan for sustainable development. Geoinformatics is also used in disaster management to assess risk, plan for emergency response, and aid in recovery efforts.
Environmental Monitoring and Disaster Management
Geoinformatics is used to monitor environmental changes, such as deforestation, erosion, and climate change. It is also used in disaster management to assess risk, plan for emergency response, and aid in recovery efforts. RS and GIS are particularly useful in this context, as they enable the rapid acquisition and analysis of large volumes of data.
C. Methods and Tools in Geoinformatics
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS is a powerful software tool that enables the storage, analysis, and visualization of spatial data. It is used to create maps, analyze patterns and trends, and identify relationships between different data layers. GIS can be used for a wide range of applications, from environmental monitoring to urban planning and development.
Remote Sensing (RS)
RS involves the use of sensors to capture data from a distance, such as from satellites or aircraft. RS is particularly useful for monitoring changes in land use, tracking changes in vegetation, and mapping natural resources. RS data can be analyzed using GIS and other data analytics tools to derive insights and inform decision-making.
Global Positioning Systems (GPS)
GPS is a network of satellites that provides precise location data. It is widely used in navigation, transportation, and logistics, as well as in environmental monitoring and disaster management. GPS receivers can be used to track the movement of vehicles, people, and animals, as well as to map natural resources and monitor environmental changes.
III. Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points
In this essay, we provided an overview of Geoinformatics, its history, applications in various industries, and the methods and tools used in the field. We discussed key concepts and terminologies, including spatial data, GIS, RS, GPS, and data analytics. We highlighted the importance of Geoinformatics in agriculture, natural resource management, urban planning and development, and disaster management.
B. Importance and Impact of Geoinformatics in Today’s Society
Geoinformatics is a rapidly evolving field that is at the forefront of technological innovation. It has the potential to revolutionize the way we study and understand the Earth’s physical and social systems. Geoinformatics enables us to map, analyze, and visualize spatial data to derive insights and make informed decisions. It is an essential tool for sustainable development, environmental monitoring, and disaster management. As we continue to face complex global challenges, the importance and impact of Geoinformatics will only continue to grow.
List of colleges and universities in India that offer Geoinformatics or related courses:
- Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay)
- Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee (IIT Roorkee)
- Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur (IIT Kanpur)
- Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur (IIT Kharagpur)
- Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS), Dehradun
- National Institute of Technology, Warangal (NIT Warangal)
- Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra
- Andhra University, Visakhapatnam
- Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi
- Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati (IIT Guwahati)
- Anna University, Chennai
- University of Delhi, Delhi
- Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh
- Jamia Millia Islamia University, New Delhi
- University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad
- Pondicherry University, Puducherry
- Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai
- University of Madras, Chennai
- Symbiosis Institute of Geoinformatics, Pune
- Indian School of Mines, Dhanbad
- University of Pune, Pune
- Gujarat Technological University, Ahmedabad
- University of Mysore, Mysore
- Gandhigram Rural Institute, Dindigul
- Kumaun University, Nainital
- North Eastern Hill University, Shillong
- University of Calcutta, Kolkata
- Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli
- Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kochi
- University of Jammu, Jammu and Kashmir
- University of Mumbai, Mumbai
- VIT University, Vellore
- Shivaji University, Kolhapur
- Tezpur University, Tezpur
- National Institute of Technology, Calicut
- Lovely Professional University, Jalandhar
- Amity University, Noida
- University of Jammu and Kashmir, Srinagar
- Manipal University, Manipal
Please note that this list is not exhaustive and there may be other colleges and universities in India that offer courses in Geoinformatics or related fields. It is recommended that you do further research and regular visit to GISvacancy.com to find the best fit for your educational goals.
some colleges and universities in India that offer Remote Sensing courses, along with the degree offered and approximate fees:
- Indian Institute of Remote Sensing, Dehradun – M.Tech Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 1.45 lakhs to INR 2.45 lakhs per year
- Anna University, Chennai – M.Tech Remote Sensing – fees range from INR 75,000 to INR 1.25 lakhs per year
- Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli – M.Sc Geoinformatics and Remote Sensing – fees range from INR 30,000 to INR 50,000 per year
- Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kochi – M.Sc Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 30,000 to INR 60,000 per year
- Andhra University, Visakhapatnam – M.Tech Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 30,000 to INR 50,000 per year
- University of Mysore, Mysore – M.Sc Geoinformatics and Remote Sensing – fees range from INR 15,000 to INR 25,000 per year
- Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi – M.Sc Environmental Sciences (Specialization in Remote Sensing and GIS) – fees range from INR 2,000 to INR 3,000 per semester
- Tezpur University, Tezpur – M.Sc in Physics (Specialization in Remote Sensing) – fees range from INR 15,000 to INR 20,000 per year
- Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, New Delhi – M.Tech Remote Sensing and Geoinformatics – fees range from INR 70,000 to INR 1.25 lakhs per year
- Punjabi University, Patiala – M.Sc Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 30,000 to INR 50,000 per year
- Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai – M.Sc Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 10,000 to INR 20,000 per year
- Symbiosis Institute of Geoinformatics, Pune – M.Sc Geoinformatics (Specialization in Remote Sensing) – fees range from INR 2.5 lakhs to INR 4 lakhs per year
- University of Delhi, New Delhi – M.Sc Geology (Specialization in Remote Sensing and GIS) – fees range from INR 20,000 to INR 30,000 per year
- Osmania University, Hyderabad – M.Tech Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 30,000 to INR 50,000 per year
- Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore – M.Tech Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 15,000 to INR 25,000 per year
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, Aurangabad – M.Sc Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 10,000 to INR 20,000 per year
- Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra – M.Sc Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 30,000 to INR 50,000 per year
- Osmania University, Hyderabad – M.Sc Geoinformatics (Specialization in Remote Sensing) – fees range from INR 20,000 to INR 30,000 per year
- Acharya Nagarjuna University, Guntur – M.Tech Remote Sensing and GIS – fees range from INR 20,000 to INR 30,000 per year
- University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad – M.Sc Geology (Specialization in Remote Sensing and GIS) – fees range from INR 10,000 to INR 20,000 per year

